What is the optimum order quantity?
The optimal order quantity is a key concept in supply chain management. It refers to the quantity of goods that a company should order in order to minimize overall costs while maximizing efficiency in inventory management.
This is the point at which the sum of ordering costs and warehousing costs is the lowest. This concept is often used in the context of inventory management in order to work economically and conserve resources.
What factors influence the optimum order quantity?
The optimum order quantity is determined by several parameters, including
- Demand for the respective product
- Delivery times of the supplier
- Storage costs for stockpiling
- Order costs per order
Precisely determining these factors helps to reduce storage and procurement costs and make the entire supply chain more efficient.
The Andler formula for calculating the optimum order quantity
The Andler formula (also known as the Wilson formula or Economic Order Quantity - EOQ) is often used to calculate the optimum order quantity. The formula is as follows:
Root of (annual requirement x order costs x 2) / (product value x inventory cost rate)
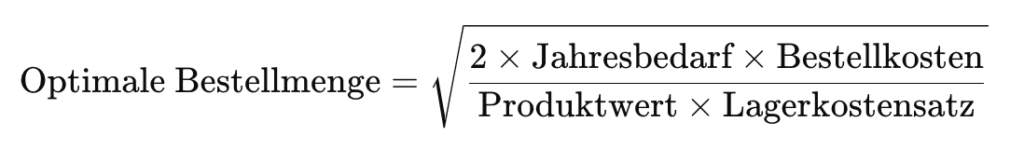
This calculation is particularly helpful for companies with constant demand and stable cost structures.
Limits of the classic calculation of the order quantity
The Andler formula provides a solid basis, but does not take into account all the influencing factors relevant in practice:
- Fluctuating demand is not included
- Varying storage or ordering costs are not taken into account
- Delivery times or their fluctuations are not shown
- Quantity discounts or price scales are missing in the calculation
Modern, dynamic processes are therefore increasingly being used.
Use of artificial intelligence to optimize the order quantity
Artificial intelligence (AI) enables a much more precise calculation of the optimum order quantity, as it:
- historical sales data,
- current stock levels,
- Delivery times,
- as well as external influencing factors such as weather, weekdays or public holidays
taken into account. AI recognizes patterns, creates demand-based forecasts and derives automated order suggestions.
The result:
- Fewer overstocks and bottlenecks
- Lower storage and ordering costs
- Greater planning and supply reliability
Target of the optimum order quantity
The main objective is to minimize the overall costs of procurement and warehousing. At the same time, a balance should be struck between sufficient availability of goods and economical warehousing.
This contributes to this:
- Avoid material bottlenecks
- Optimum use of storage capacities
- make operational processes more efficient
Advantages of the optimum order quantity procedure
Using the optimum order quantity has numerous advantages:
- Reduction of total costs in warehousing and procurement
- Improved inventory planning thanks to a sound basis for decision-making
- More efficient processes in purchasing and warehouse management
- Strengthening the entire supply chain performance
Importance of the optimum order quantity for the food industry
Precisely determining the optimum order quantity is particularly relevant in the food retail and catering sectors - especially due to the short shelf life of many products.
- Too low an order quantity leads to bottlenecks and loss of sales
- Ordering too much causes unnecessary storage costs and food waste
Demand-oriented planning and precise forecasting can reduce costs, promote sustainability and improve the availability of goods.
Request a callback
We will be happy to call you back promptly to talk to you personally









